Ever found yourself scratching your head over what canonical tags are and why they matter? In “What Are Canonical Tags?”, you’ll dive into a simple yet comprehensive explanation of these often-overlooked pieces of HTML code. You’ll learn how canonical tags help search engines understand the primary version of a duplicated webpage, ensuring your site gets the SEO credit it deserves. By the end of the article, you’ll know how to implement these tags effectively, ultimately boosting your site’s visibility and ranking. Have you ever wondered if there’s a way to tell search engines that certain URLs on your website are identical? Or maybe you have had issues with duplicate content affecting your SEO ranking? Well, that’s where canonical tags come in.
Understanding Canonical Tags
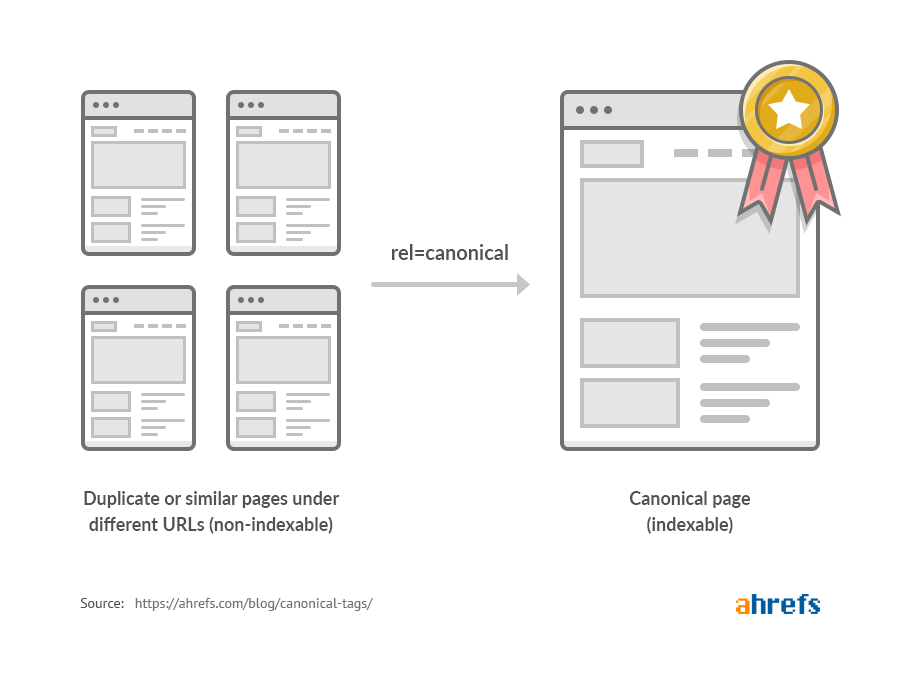
What Are Canonical Tags?
Simply put, canonical tags are a way to tell search engines which version of a URL you want to be the main one. They are a crucial part of your SEO toolkit. These tags help to prevent issues related to duplicate content by indicating the “canonical” or “preferred” version of a webpage.
Why Are Canonical Tags Important?
Canonical tags help search engines understand which URL represents the master copy of your content. This not only improves your site’s SEO but also enhances the user experience by ensuring that visitors always find the most relevant and up-to-date content.
How Do Canonical Tags Work?
Mechanism of Canonical Tags
When you add a canonical tag to a webpage, you’re essentially saying, “Hey, search engines! This is the main version of this page.” This helps to consolidate your page’s ranking signals and avoid having multiple URLs with duplicate content competing against each other.
Where to Place Canonical Tags
Canonical tags should be placed within the section of your HTML. This placement ensures that search engines find and interpret the tag correctly when they crawl your site.
Here’s a simple example of a canonical tag:
Canonical Tags vs. Noindex Tags
It’s easy to confuse canonical tags with noindex tags, but they serve different purposes. While canonical tags indicate the preferred version of a page, noindex tags instruct search engines not to index a page at all.
The table below encapsulates the primary differences:
| Feature | Canonical Tags | Noindex Tags |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Point to the preferred version of a page | Prevent indexing of a page |
| Location in HTML | Inside the | Inside the |
| Impact on SEO | Consolidates indexing signals | Page does not appear in search results |
| Use Cases | Duplicate content scenarios | Pages that should remain out of search |
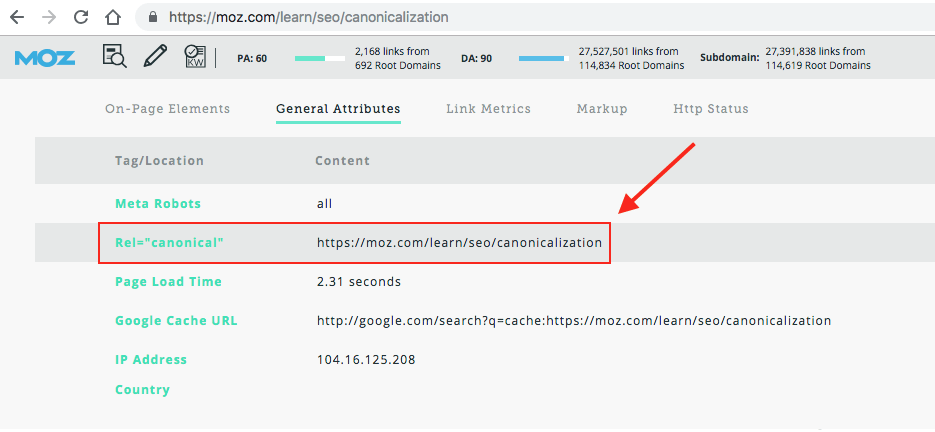
Common Use Cases for Canonical Tags
Duplicate Content
One of the most common uses for canonical tags is to manage duplicate content. Whether you have different URLs for the same content or variations like print-friendly versions, canonical tags can streamline these into one preferred URL.
Consolidating Versions of a Page
Sometimes, users can access the same content through different paths or URLs. For instance:
-
https://example.com/page -
https://example.com/page?ref=123 -
https://example.com/page/index.html
Using canonical tags, you can point all these variations to a single preferred URL.
Syndicated Content
If you’re syndicating your content across multiple platforms, you’ll want to use canonical tags to ensure that your original content gets the credit. This way, search engines give precedence to your site, not third-party websites.
How to Implement Canonical Tags
Step-by-Step Guide to Adding Canonical Tags
Adding canonical tags may seem daunting, but it’s quite straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Identify Duplicate Content:
- Use tools like Google Search Console or third-party SEO tools to find duplicate content on your site.
Choose the Preferred URL:
- Decide which version you want to be the canonical version.
Add the Canonical Tag:
- Insert the canonical tag in the
section of the non-canonical pages.
- Insert the canonical tag in the
Example:
Test Your Implementation:
- Use tools like Google Search Console to check if your canonical tags are set up correctly.
Monitor and Adjust:
- Regularly check the performance and make adjustments as needed.
Tools to Help with Canonical Tag Implementation
There are several tools you can use to help with the implementation and monitoring of canonical tags:
- Google Search Console
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- Ahrefs Site Audit
- SEMrush Site Audit
These tools can help identify issues and ensure that your canonical tags are properly set up.
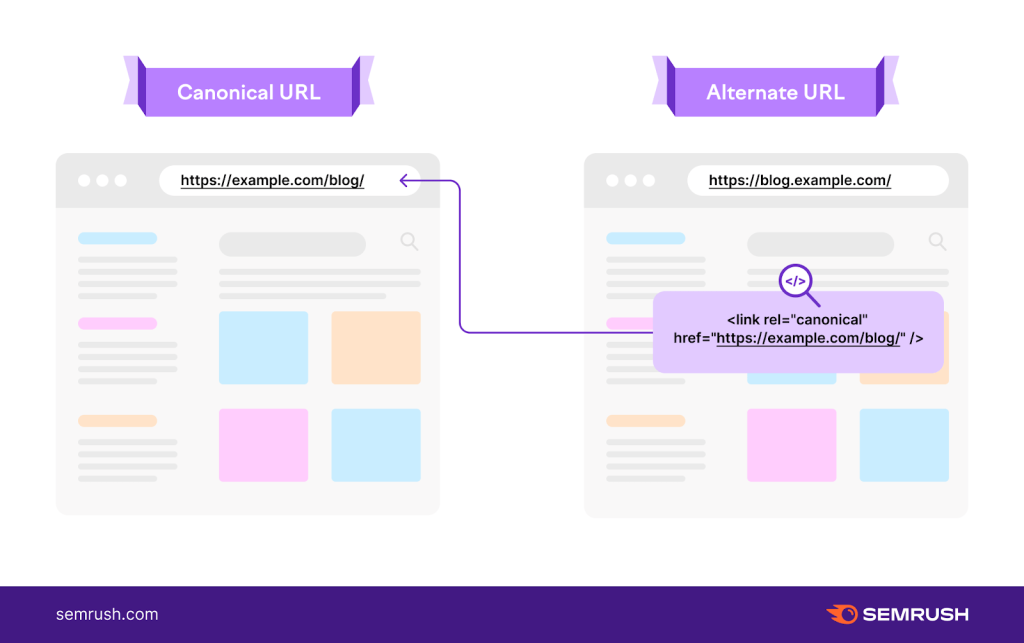
Best Practices for Using Canonical Tags
Consistency is Key
Ensure that your canonical tags are consistent across your site. This consistency helps search engines easily understand which page is the preferred version.
Use Absolute URLs
Always use absolute URLs (including the protocol and domain) for canonical tags. This practice prevents any ambiguity about which version of the page is canonical.
Avoid Self-Referencing When Possible
While self-referencing canonical tags (a canonical tag pointing to the same URL) are generally safe, they can sometimes be unnecessary. Focus on using canonical tags to point out duplicates rather than self-referencing by default.
Troubleshooting Canonical Tag Issues
Common Problems and Fixes
Here are some common issues you might encounter with canonical tags and how to fix them:
Misconfigured Tags
Ensure the canonical tags are pointing to the correct URLs. Misconfiguring tags can lead to search engines indexing the wrong page.
Fix: Double-check URLs in the canonical tags and use tools to verify configurations.
Conflicting Tags
Avoid having multiple canonical tags on a single page. This can confuse search engines.
Fix: Review your HTML to ensure only one canonical tag is present.
Non-Canonical Pages Indexed
Despite having canonical tags, sometimes search engines index non-canonical pages. This situation could be due to issues with crawl budgets or other SEO factors.
Fix: Regularly monitor performance and make necessary adjustments.
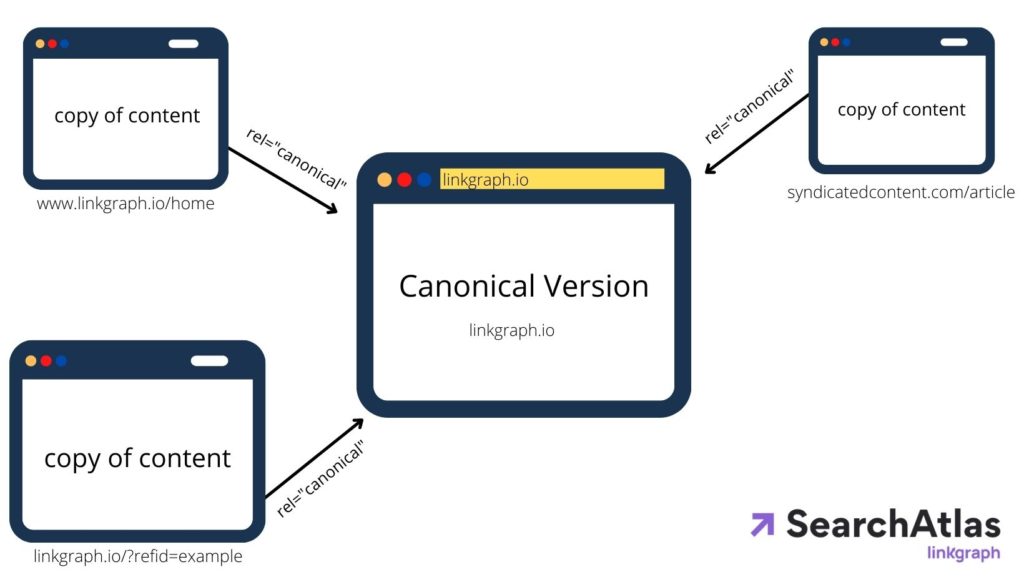
Canonical Tags in Relation to Other SEO Practices
Interaction with Hreflang Tags
Canonical tags and hreflang tags (used for international SEO) can coexist but need careful implementation. Ensure that hreflang tags point to the correct language/region versions and that canonical tags align with the preferred versions for those regional pages.
Canonical Tags and 301 Redirects
While 301 redirects permanently move a URL and pass its ranking signals to the new URL, canonical tags simply indicate the preferred version. Use 301 redirects for permanent moves and canonical tags for managing duplicate content.
Frequently Asked Questions About Canonical Tags
Can Canonical Tags Be Used Across Domains?
Yes, you can use cross-domain canonical tags if your content is duplicated across different domains. This helps search engines recognize the original source.
Do Canonical Tags Affect Page Load Speed?
Canonical tags are a lightweight code addition to your page and have negligible impact on page load speed.
Should Canonical Tags Be Used for Pagination?
Canonical tags should not be used for paginated content. Instead, use rel="next" and rel="prev" tags to indicate the sequence of the pages.
Conclusion
Canonical tags are a powerful tool in managing duplicate content and improving your website’s SEO. By guiding search engines to the preferred versions of your pages, you ensure a more streamlined and efficient crawl of your site. Plus, implementing them correctly is fairly straightforward, and various tools are available to aid in the process.
So, next time you’re optimizing your website, don’t overlook the importance of canonical tags. They might just be the SEO boost you’re looking for!